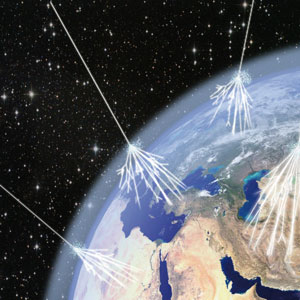
Astroparticle physics includes a vast field of research with experiments conducted mostly without accelerators on cosmic radiation, neutrinos, gravitation and quantum mechanics.
Consequently, also the used experimental techniques are very heterogeneous, ranging from lasers to the use of low activity materials, from cryogenics to the particle detectors used in other lines of research.
The experiments may be of small size (“table-top”) or extend over areas of several km2, situated in space or under the sea, in underground laboratories or in the Antarctic ice.
The discovery of cosmic radiation dates back to 1912 and for many years, before the use of accelerators, allowed us to discover new hitherto unknown particles (just think of the “positron”, i.e. the anti-electron).
Although research in the astroparticle physics field has spanned more than a century, it is still a research sector full of new and exciting discoveries (just think of the recent observation of gravitational waves by the LIGO experiment), in which the National Institute for Nuclear Physics is engaged since decades. In particular, researchers of the Frascati National Laboratories are involved in neutrino studies and in space research.
For further information:
http://home.infn.it/it/ INFN official website.
http://www.asimmetrie.it/ INFN magazine, with a number of monographs on the subject.
NAUTILUS
At the Frascati Laboratories, NAUTILUS, a gravitational wave detector consisting of a 2.3 ton resonant bar at a temperature of only 0.13 degrees above absolute zero, has been in operation since 1995. The detector was designed to detect gravitational waves emitted by high-frequency sources (around 1 kHz), such as gravitational collapses with the formation of neutron stars or blacks holes.
QUAX
The QUAX (QUest for AXions) experiment looks for the presence in our galaxy of hypothetical particles called axions which could constitute the dark matter.
CUORE
CUORE is a second-generation experiment for research in Double Beta Decay of 130Te without neutrino emission. The sensitivity is such as to allow probing of the mass region of the neutrino suggested for inverse hierarchy by the results of the most recent experiments on neutrino oscillations.
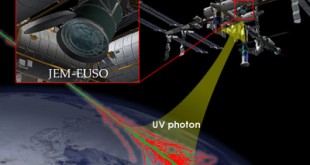
Jem-EUSO
JEM-EUSO is an international project aimed at the building of a long lasting space observatory dedicated to the study and detection of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays (UHECR) and E > 100 EeV energy neutrinos. Thanks to the study of the nature and origin of UHECR basic fundamental physics and high energy astrophysics problems have been addressed.
KM3NeT
KM3NeT is a research infrastructure being installed deep in the Mediterranean Sea. The infrastructure houses neutrino telescopes composed of arrays of thousands of optical sensors capable of seeing the weak Cerenkov light generated by the collision of neutrinos with the water of the sea depths.
JUNO
JUNO is an experiment dedicated to the measurement of the neutrino mass hierarchy, one of the main issues still open in particle physics. It is located in the Popular Republic of China, near Jiangmen town, 50 km away from two nuclear power plants, providing 26.6 GW starting from 2020.
MoonLIGHT-2
The MoonLIGHT-2 collaboration aims to study the physics of gravitation by measuring, using the Laser Ranging technique (possibly coupled with Microwave Ranging measurements), the distance between the Earth and other celestial bodies (namely, the Moon and Mars).
OPERA (LNGS)
Neutrinos are fundamental particles with very small mass and no electric charge. In nature there are three types and as a consequence of quantum mechanics they can oscillate from one type to another. The OPERA experiment, situated at the Gran Sasso underground laboratories, has been designed to directly observe the oscillation of muon neutrinos from the CNGS beam produced at CERN into tau neutrinos.
SIMP
Many questions that today’s physics poses, from the nature of dark matter to the properties of the quantum vacuum, require to detect electromagnetic signals with energy under the millielectronvolt (a thousand times less energetic than visible light) and of very low intensity, up to the limit of the single photon.
Wizard/PAMELA
WIZARD is an experimental program dedicated to the study of Cosmic Rays in a wide energy range (from a few dozens of MeV to a few hundreds of GeV), with especial focus on possible Dark Matter marks and Antimatter components: positrons, antiprotons and the search for antinuclei.
LIMADOU
CSES (China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite) – LIMADOU is a program of scientific space missions dedicated to monitoring electromagnetic field and waves, plasma and particle perturbations of the atmosphere, ionosphere and magnetosphere induced by natural sources and anthropocentric emitters and to study their correlations with the occurrence of seismic events.
DarkSide
DarkSide is an experiment that aims to reveal dark matter particles. The experiment is located at Gran Sasso National Laboratories and uses a dual-phase TPC filled with liquid argon depleted in 39Ar as a detector.
CYGNO
CYGNO is a detector under construction at INFN Frascati National Laboratories for the detection of dark matter and neutrinos coming from the Sun. Its main characteristic is the ability to see - like a telescope - in a determined direction.
 INFN-LNF Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati
INFN-LNF Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati